1, The working principle of the piston compressor is the cylinder, valve and in the cylinder for the reciprocating movement of the piston constituted by the work volume constantly changing to complete. If you do not consider the actual work of the piston compressor volume loss and energy loss (that is, the ideal work process), the piston compressor crankshaft per rotation of a week to complete the work, can be divided into suction, compression and exhaust process.
Compression process: the piston from the lower stop point upward movement, suction and discharge valve in the closed state, the gas in the closed cylinder is compressed, as the cylinder volume gradually reduced, the pressure, temperature gradually increased until the cylinder gas pressure and exhaust pressure equal. Compression process is generally regarded as isentropic process.
Exhaust process: the piston continues to move upward, resulting in the cylinder gas pressure is greater than the exhaust pressure, the exhaust valve opens, the cylinder gas in the piston to push the pressure out of the cylinder into the exhaust pipe, until the piston movement to the upper stop. At this point, due to the exhaust valve spring force and the role of gravity of the valve itself, the exhaust valve closed exhaust end.
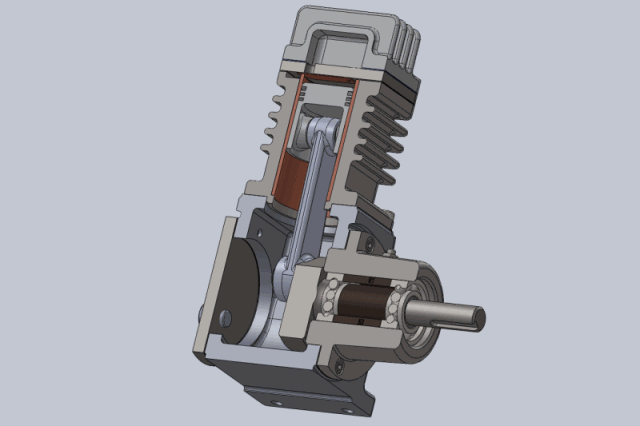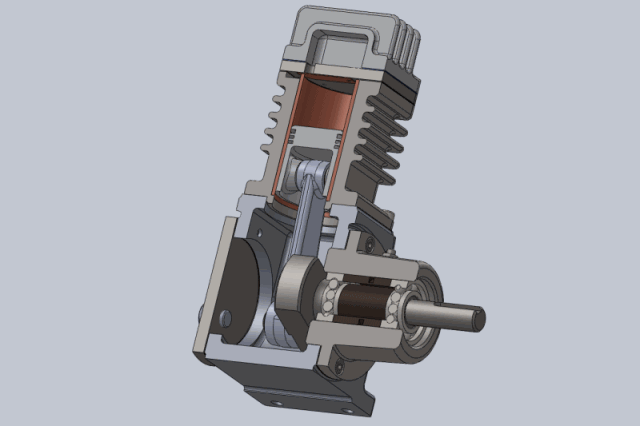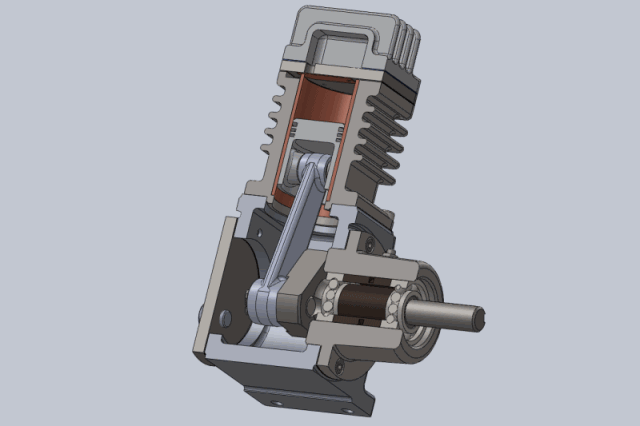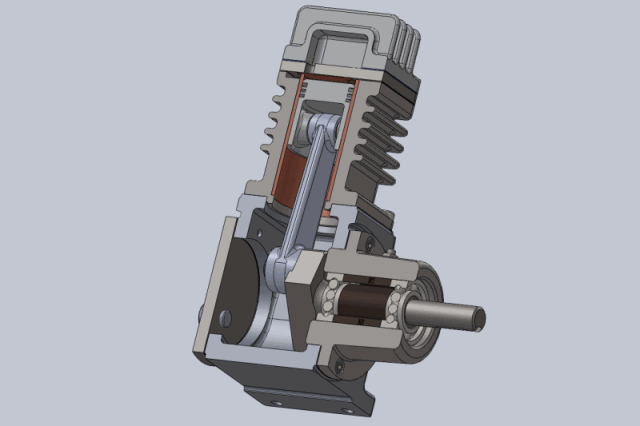
2, piston compressor applications
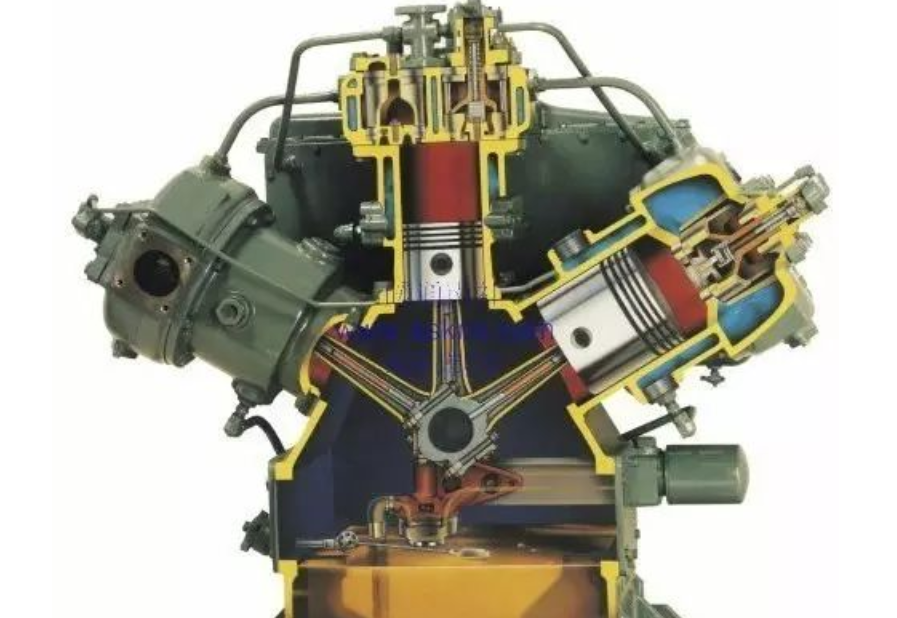
Main applications: cold storage and freezing and refrigerating market use more semi-hermetic piston compressors; lesser applications: commercial refrigeration air conditioning.
Semi-hermetic piston compressor for cold storage is generally driven by a four-pole motor, and its rated power is generally between 60-600 KW. The number of cylinders is 2 - 8, up to 12. 2, piston compressor applications
The main applications: cold storage and refrigeration and freezing market use more semi-hermetic piston compressor; lesser applications: commercial refrigeration air conditioning.
Semi-hermetic piston compressor for cold storage is generally driven by a four-pole motor, and its rated power is generally between 60-600KW. The number of cylinders is 2 - 8, up to 12.

3, the advantages of piston compressors
(1) The required pressure can be obtained regardless of the flow rate, with a wide range of discharge pressures up to 320MPa (industrial applications) and even 700MPa, (in the laboratory).
(2) Single machine capacity for any flow rate up to 500 m3/min.
(3) Low material requirements in the general pressure range, mostly made of common steel materials, easier to process and cheaper to build.
(4) Higher thermal efficiency, generally large and medium-sized units can reach about 0.7~0.85 adiabatic efficiency.
(5) Strong adaptability when adjusting the gas volume, i.e. the exhaust range is wider and not affected by the high or low pressure, and it can adapt to a wider pressure range and refrigeration volume requirements.
(6) The heaviness and characteristics of the gas have little influence on the working performance of the compressor, and the same compressor can be used for different gases.
(7) The drive machine is relatively simple, mostly using electric motors, generally without speed regulation, and is highly serviceable.
(8) piston compressor technology is more mature, the production of the use of the accumulated experience.
4, the disadvantages of piston compressors
(1) complex and bulky structure, wearing parts, large floor space, high investment, maintenance workload, the use of a shorter cycle, but after efforts can reach more than 8000 hours.
(2) The speed is not high, the machine is large and heavy, and the exhaust volume of a single machine is generally less than 500 m3/min.
(3) Vibration in the operation of the machine.
(4) Exhaust gas is not continuous, the airflow has pulsation, which is easy to cause vibration of the pipe, often causing damage to the pipe network or machine parts due to airflow pulsation and resonance in serious cases.
(5) Flow regulation using subsidized volume or bypass valves, although simple, convenient and reliable, but with large power losses and reduced efficiency during partial load operation.
(6) Oil-lubricated compressors with oil in the gas that needs to be removed.
(7) Large plants using multiple compressor sets when there are many operators or work intensity is high.
Post time: Aug-03-2022






